
The Johari Window model was developed by two psychologists. Interestingly, they called their Johari Window model “Johari” after combining their first names, Joe and Harry (Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham).
The Johari Window model consists of four quadrants. Each of these quadrants contains and represents information known about the person, in terms of whether the information is known or unknown by the person, and whether the information is known or unknown by others. The Johari Window’s four quadrants are described as follows:
- Open (Public) Area: what is known by the person about him/herself and is also known by others.
- Blind Area (spot): what is known by others but is unknown by the person about him/herself.
- Hidden Area: what the person knows about him/herself that is unknown to others.
- Unknown (Unconscious) Area: what is unknown by the person about him/herself and is also unknown by others.
The Johari Window is drawn like a window with four panes, with each of the panes, or quadrants, labeled as follows:
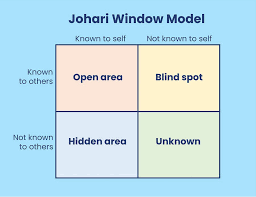
The Johari Window model is a constructive means for exemplifying and enhancing self-awareness, and communal understanding between individuals within a group. The Johari Window model can also be used to evaluate and grow a group’s relationship with other groups.
Image source: https://fundakoca.medium.com/johari-window-9f874884fc10


This is excellent model to introduce on group therapy. Allow members to discuss their involvement in group as it pertains to each window. By giving open self members can free themselves of wasted energy to keep secrets. When members gently and specifically confront each other they open up their self knowledge.